The temperature in Calgary gets down to -40 degrees Celcius in the winter and the water board’s staff are fully occupied in winter, however in summer they have surplus staff and only 4 staff trained in leak detection. With thousands of fittings to survey in a very short summer it would not be possible for these 4 operators to survey a substancial part of the network or worth trying to train more operators.
Hydrosave developed a leak detection methodology that enabled the in-experienced surplus staff to go and perform an acoustic sounding survey listening on all fittings and recording the noise levels produced by the Aquascope 3. The operators were sent out without the headphones and the values recorded were used to localise the leak positions using noise clustering principals.
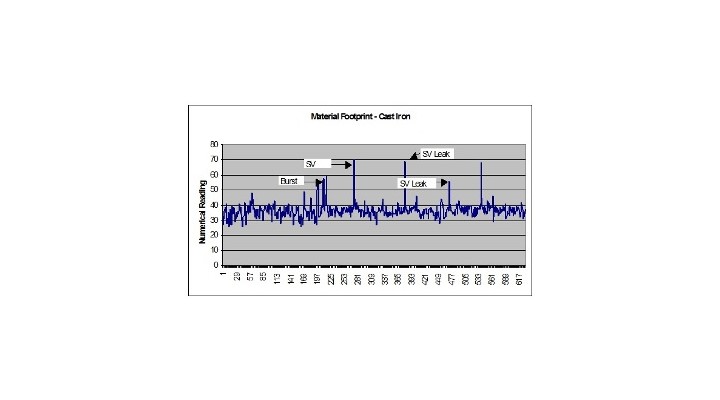
The average daily distance listening on all fittings was 5.8km/day and the average daily distance listening on fire hydrants only was 14.2km/day. Once the operator returned, all of the sounding levels collected we entered into a computer sequentially and displayed graphically. An example of one of these graphs can be seen in Figure 3. The spikes in the graph indicate areas of interest where investigation is required to determine if a leak is in the area.
The skilled leakage operators investigated and pinpointed the leaks at the sites identified as having higher noise levels with the Aquascope 3 ground microphone.
This localisation technique proved to be extremley effective and maximised the efficiency of the skilled and un-skilled operators.